
MSA 아키텍처에서 Redis가 싱글쓰레드를 이용해서 처리가 되기 때문에 원자성(atomic)보장!
즉, 데이터 정합성이 깨지지 않습니다!
그래서 커머스 같은 곳에서는 재고처리를 Redis로 하는데..
그런데 말입니다! 잘나가는 커머스는 대용량 트래픽 일텐데 이걸 버텨낸다?? 싱글쓰레드인데?
왜 성능이 좋은지 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
Redis의 성능적 비밀은? Multiplexing / Event Loop

사실 아니 어떻게 싱글쓰레드가 대용량 트래픽을 받는다는거지? 라는 의문이 생겨서 찾아보게 되고 포스팅을 하게 되었습니다.
알고봤더니 다이렉트로 싱글 쓰레드가 받아서 처리하는 구조가 아니였습니다!!

위 그림의 I/O Multiplexing을 살펴봅시다!
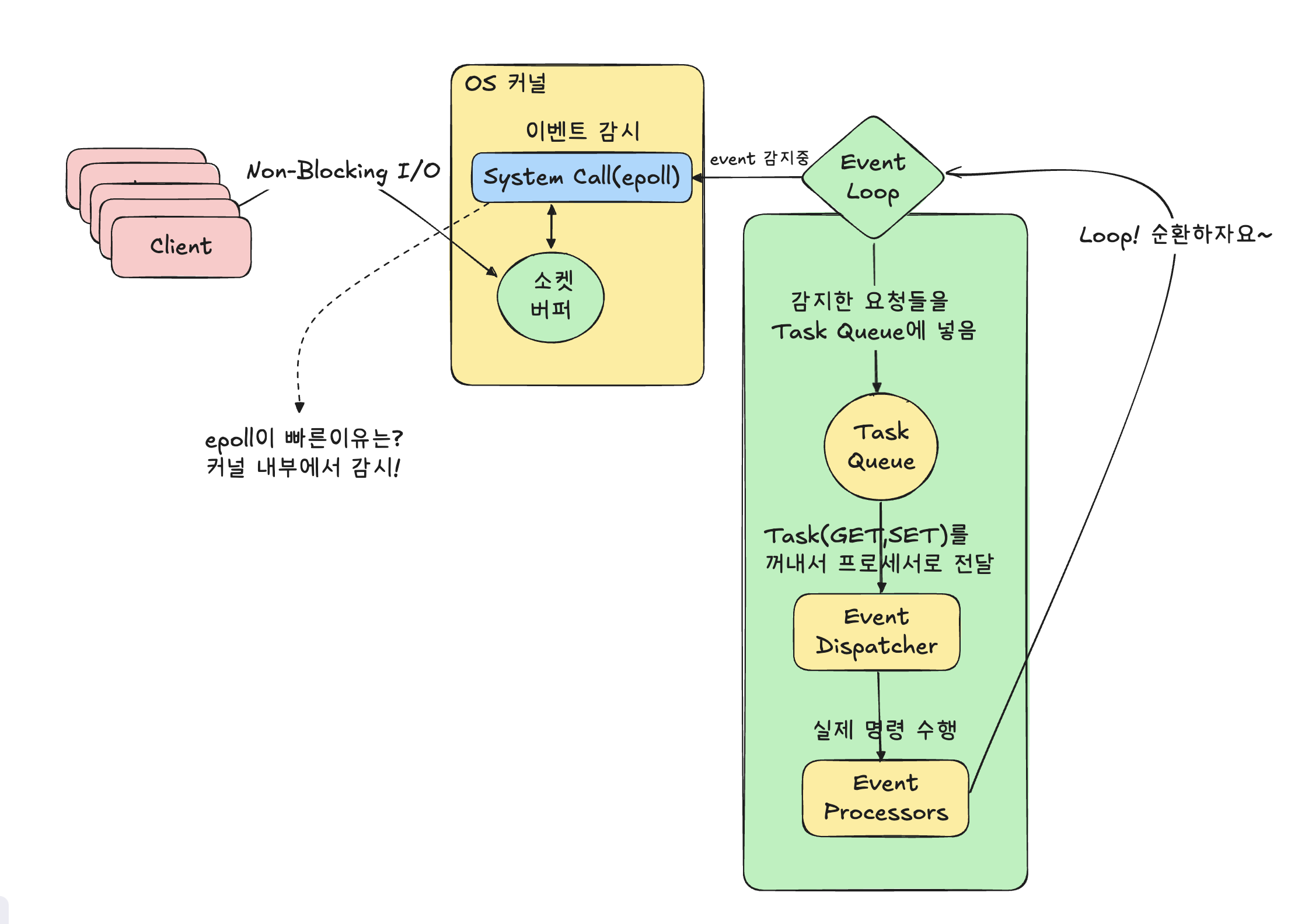
1) 클라이언트 : A,B,C 클라이언트가 동시에 Redis 서버에 요청을 보냅니다.(NoN-Blocking I/O)
2) I/O Multiplex Connections
시스템 콜을 사용!(select, poll, epoll) : 여러 소켓(클라이언트)을 감시하고
어떤 클라이언트의 소켓에 읽기/쓰기 이벤트가 발생했는지를 OS 수준에서 알려줍니다.
즉, A클라이언트에서 읽을수 있는 데이터가 있는지 혹은 B클라이언트가 응답이 가능한지 등을 감지 합니다.
그리고 여러 연결을 동시에 감시하지만 실제처리는 한 쓰레드(Event Loop)가 담당 합니다. (3번)
3) Event Loop
이벤트 루프는 감지된 이벤트를 하나씩 순서대로 꺼내와서 처리 합니다.
ex) Client A -> 읽기 요청 발생 / Client B -> 쓰기 요청 발생
이런식으로 큐에 쌓인 이벤트를 차례로 확인 합니다.
Redis는 싱글쓰레드이지만 이벤트 루프가 빠르게 순환하면서 여러 연결을 처리하므로 사실상 병렬처럼 느껴집니다.
3-1) Task Queue
이벤트 루프에서 감지한 요청들을 작업단위(Task)로 큐에 넣습니다. (GET, SET, INCR 등)
3-2) Event Dispatcher
Task Queue에 있는 작업을 꺼내서 적절한 이벤트 프로세서로 전달 합니다.
Redis 내부에서는 명령어별로 처리 로직이 정해져있습니다.(SET:저장, GET: 조회)
3-3) Event Processors
실제 명령을 실행하고 결과를 반환하는 부분 입니다.
모든 처리는 원자적(Atomic)으로 수행 됩니다.
완료 후 읽기라면 응답이 클라이언트로 데이터를 보내야하는데 이때는 Write 이벤트를 만들고 Event Loop를 통해서
클라이언트에게 응답 합니다.
핵심은 I/O 멀티플렉스 커넥션으로 여러 클라이언트 연결을 동시에 감시!
그리고 이벤트 루프를 통한 이벤트 순환처리라고 볼수 있습니다.

System Call(select, poll, epoll)
OS레벨의 System Call은 OS마다 다릅니다. 그래서 select, poll, epoll 3개를 언급!
select
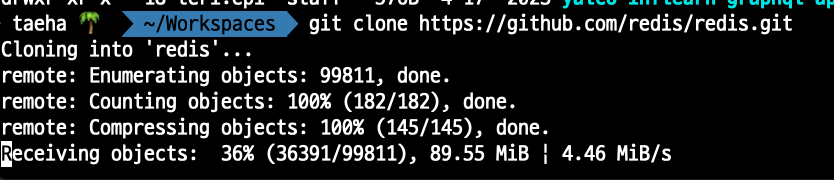
Redis Source를 다운받아봅니다.
git clone https://github.com/redis/redis.git
branch가 unstable??

git tag로 뭐가 있는지 확인 합니다.

https://github.com/redis/redis/releases 에 가보면 가장 최신이 뭔지 확인 한 뒤에 checkout을 해줍니다.

최신버전이 있는지 확인 합니다.

-int는 internal / integration 버전으로 공식 버전 전 테스트용 입니다.
즉, 다음 메이저 릴리즈를 위한 개발 중간 단계 버전 입니다.
-rc는 release candidate(릴리즈 후보)
최신버전 8.2.2을 사용해봅시다!
git checkout 8.2.2
대충 커밋하려면 새로운 브랜치를 만들라고 하는데 코드만 살펴볼꺼니 걍 사용합니다.

code는 아래와 같이 되어있습니다. 이제 인텔리J같은 IDE를 통해 Redis의 시스템 콜 하는 소스가 있는지 찾아보아요~
그런데 아래에 보니 Makefile이 있네요
Redis는 C계열 언어로 만들어진거 같습니다.
make를 통해 실행파일을 만들어보겠습니다.
make 수행!

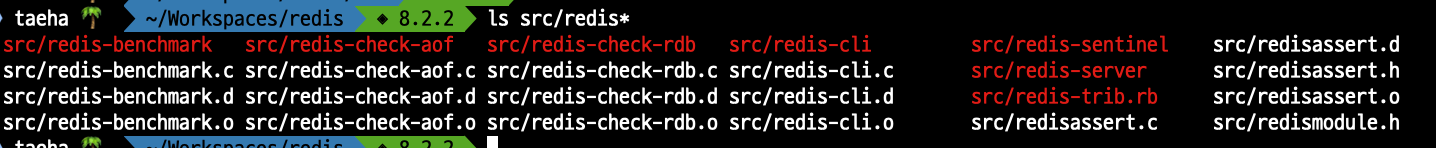
ls src/redis* 로 해보면 여러 실행파일들이 생성되었습니다.
src/redis-cli src/redis-server 등등
기존에는 뭐가 있었는지 make clean을 통해 초기상태로 돌리고 확인해보겠습니다.

기존에는 아래의 파일들만 있었습니다.
다시 돌아와서 소스를 찾아보도록 하겠습니다.

epoll로 조회 해봅니다.
ae_epoll.c

*eventLoop의 객체를 넘겨받아서 뭔가 할당을 해줍니다.
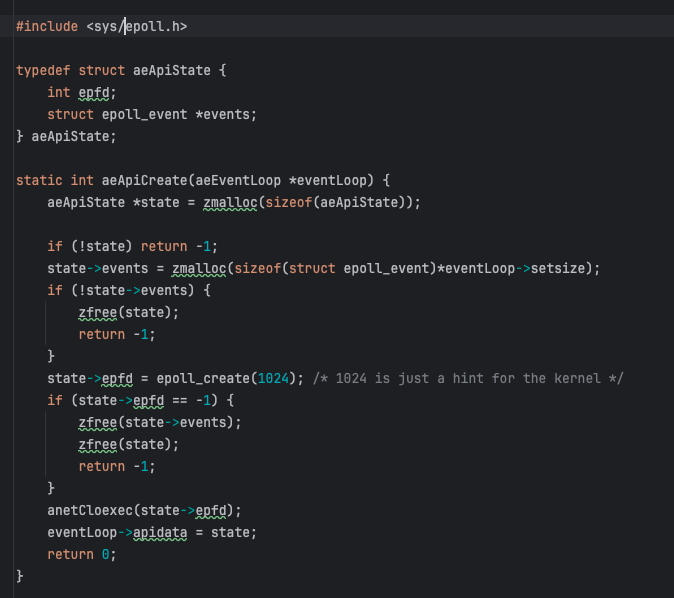
/* Linux epoll(2) based ae.c module
*
* Copyright (c) 2009-Present, Redis Ltd.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Licensed under your choice of (a) the Redis Source Available License 2.0
* (RSALv2); or (b) the Server Side Public License v1 (SSPLv1); or (c) the
* GNU Affero General Public License v3 (AGPLv3).
*/
#include <sys/epoll.h>
typedef struct aeApiState {
int epfd;
struct epoll_event *events;
} aeApiState;
static int aeApiCreate(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
aeApiState *state = zmalloc(sizeof(aeApiState));
if (!state) return -1;
state->events = zmalloc(sizeof(struct epoll_event)*eventLoop->setsize);
if (!state->events) {
zfree(state);
return -1;
}
state->epfd = epoll_create(1024); /* 1024 is just a hint for the kernel */
if (state->epfd == -1) {
zfree(state->events);
zfree(state);
return -1;
}
anetCloexec(state->epfd);
eventLoop->apidata = state;
return 0;
}
static int aeApiResize(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int setsize) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
state->events = zrealloc(state->events, sizeof(struct epoll_event)*setsize);
return 0;
}
static void aeApiFree(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
close(state->epfd);
zfree(state->events);
zfree(state);
}
static int aeApiAddEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
struct epoll_event ee = {0}; /* avoid valgrind warning */
/* If the fd was already monitored for some event, we need a MOD
* operation. Otherwise we need an ADD operation. */
int op = eventLoop->events[fd].mask == AE_NONE ?
EPOLL_CTL_ADD : EPOLL_CTL_MOD;
ee.events = 0;
mask |= eventLoop->events[fd].mask; /* Merge old events */
if (mask & AE_READABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLIN;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLOUT;
ee.data.fd = fd;
if (epoll_ctl(state->epfd,op,fd,&ee) == -1) return -1;
return 0;
}
static void aeApiDelEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int delmask) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
struct epoll_event ee = {0}; /* avoid valgrind warning */
int mask = eventLoop->events[fd].mask & (~delmask);
ee.events = 0;
if (mask & AE_READABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLIN;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLOUT;
ee.data.fd = fd;
if (mask != AE_NONE) {
epoll_ctl(state->epfd,EPOLL_CTL_MOD,fd,&ee);
} else {
/* Note, Kernel < 2.6.9 requires a non null event pointer even for
* EPOLL_CTL_DEL. */
epoll_ctl(state->epfd,EPOLL_CTL_DEL,fd,&ee);
}
}
static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
int retval, numevents = 0;
retval = epoll_wait(state->epfd,state->events,eventLoop->setsize,
tvp ? (tvp->tv_sec*1000 + (tvp->tv_usec + 999)/1000) : -1);
if (retval > 0) {
int j;
numevents = retval;
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
int mask = 0;
struct epoll_event *e = state->events+j;
if (e->events & EPOLLIN) mask |= AE_READABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLOUT) mask |= AE_WRITABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLERR) mask |= AE_WRITABLE|AE_READABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLHUP) mask |= AE_WRITABLE|AE_READABLE;
eventLoop->fired[j].fd = e->data.fd;
eventLoop->fired[j].mask = mask;
}
} else if (retval == -1 && errno != EINTR) {
panic("aeApiPoll: epoll_wait, %s", strerror(errno));
}
return numevents;
}
static char *aeApiName(void) {
return "epoll";
}poll로 조회해보니 ae.c라는게 나옵니다.
/* A simple event-driven programming library. Originally I wrote this code
* for the Jim's event-loop (Jim is a Tcl interpreter) but later translated
* it in form of a library for easy reuse.
*
* Copyright (c) 2006-Present, Redis Ltd.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Licensed under your choice of (a) the Redis Source Available License 2.0
* (RSALv2); or (b) the Server Side Public License v1 (SSPLv1); or (c) the
* GNU Affero General Public License v3 (AGPLv3).
*/
#include "ae.h"
#include "anet.h"
#include "redisassert.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include "zmalloc.h"
#include "config.h"
/* Include the best multiplexing layer supported by this system.
* The following should be ordered by performances, descending. */
#ifdef HAVE_EVPORT
#include "ae_evport.c"
#else
#ifdef HAVE_EPOLL
#include "ae_epoll.c"
#else
#ifdef HAVE_KQUEUE
#include "ae_kqueue.c"
#else
#include "ae_select.c"
#endif
#endif
#endif
#define INITIAL_EVENT 1024
aeEventLoop *aeCreateEventLoop(int setsize) {
aeEventLoop *eventLoop;
int i;
monotonicInit(); /* just in case the calling app didn't initialize */
if ((eventLoop = zmalloc(sizeof(*eventLoop))) == NULL) goto err;
eventLoop->nevents = setsize < INITIAL_EVENT ? setsize : INITIAL_EVENT;
eventLoop->events = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFileEvent)*eventLoop->nevents);
eventLoop->fired = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFiredEvent)*eventLoop->nevents);
if (eventLoop->events == NULL || eventLoop->fired == NULL) goto err;
eventLoop->setsize = setsize;
eventLoop->timeEventHead = NULL;
eventLoop->timeEventNextId = 0;
eventLoop->stop = 0;
eventLoop->maxfd = -1;
eventLoop->beforesleep = NULL;
eventLoop->aftersleep = NULL;
eventLoop->flags = 0;
memset(eventLoop->privdata, 0, sizeof(eventLoop->privdata));
if (aeApiCreate(eventLoop) == -1) goto err;
/* Events with mask == AE_NONE are not set. So let's initialize the
* vector with it. */
for (i = 0; i < eventLoop->nevents; i++)
eventLoop->events[i].mask = AE_NONE;
return eventLoop;
err:
if (eventLoop) {
zfree(eventLoop->events);
zfree(eventLoop->fired);
zfree(eventLoop);
}
return NULL;
}
/* Return the current set size. */
int aeGetSetSize(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
return eventLoop->setsize;
}
/*
* Tell the event processing to change the wait timeout as soon as possible.
*
* Note: it just means you turn on/off the global AE_DONT_WAIT.
*/
void aeSetDontWait(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int noWait) {
if (noWait)
eventLoop->flags |= AE_DONT_WAIT;
else
eventLoop->flags &= ~AE_DONT_WAIT;
}
/* Resize the maximum set size of the event loop.
* If the requested set size is smaller than the current set size, but
* there is already a file descriptor in use that is >= the requested
* set size minus one, AE_ERR is returned and the operation is not
* performed at all.
*
* Otherwise AE_OK is returned and the operation is successful. */
int aeResizeSetSize(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int setsize) {
if (setsize == eventLoop->setsize) return AE_OK;
if (eventLoop->maxfd >= setsize) return AE_ERR;
if (aeApiResize(eventLoop,setsize) == -1) return AE_ERR;
eventLoop->setsize = setsize;
/* If the current allocated space is larger than the requested size,
* we need to shrink it to the requested size. */
if (setsize < eventLoop->nevents) {
eventLoop->events = zrealloc(eventLoop->events,sizeof(aeFileEvent)*setsize);
eventLoop->fired = zrealloc(eventLoop->fired,sizeof(aeFiredEvent)*setsize);
eventLoop->nevents = setsize;
}
return AE_OK;
}
void aeDeleteEventLoop(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
aeApiFree(eventLoop);
zfree(eventLoop->events);
zfree(eventLoop->fired);
/* Free the time events list. */
aeTimeEvent *next_te, *te = eventLoop->timeEventHead;
while (te) {
next_te = te->next;
if (te->finalizerProc)
te->finalizerProc(eventLoop, te->clientData);
zfree(te);
te = next_te;
}
zfree(eventLoop);
}
void aeStop(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 1;
}
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask,
aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData)
{
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) {
errno = ERANGE;
return AE_ERR;
}
/* Resize the events and fired arrays if the file
* descriptor exceeds the current number of events. */
if (unlikely(fd >= eventLoop->nevents)) {
int newnevents = eventLoop->nevents;
newnevents = (newnevents * 2 > fd + 1) ? newnevents * 2 : fd + 1;
newnevents = (newnevents > eventLoop->setsize) ? eventLoop->setsize : newnevents;
eventLoop->events = zrealloc(eventLoop->events, sizeof(aeFileEvent) * newnevents);
eventLoop->fired = zrealloc(eventLoop->fired, sizeof(aeFiredEvent) * newnevents);
/* Initialize new slots with an AE_NONE mask */
for (int i = eventLoop->nevents; i < newnevents; i++)
eventLoop->events[i].mask = AE_NONE;
eventLoop->nevents = newnevents;
}
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];
if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1)
return AE_ERR;
fe->mask |= mask;
if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc;
fe->clientData = clientData;
if (fd > eventLoop->maxfd)
eventLoop->maxfd = fd;
return AE_OK;
}
void aeDeleteFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask)
{
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) return;
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];
if (fe->mask == AE_NONE) return;
/* We want to always remove AE_BARRIER if set when AE_WRITABLE
* is removed. */
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) mask |= AE_BARRIER;
aeApiDelEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask);
fe->mask = fe->mask & (~mask);
if (fd == eventLoop->maxfd && fe->mask == AE_NONE) {
/* Update the max fd */
int j;
for (j = eventLoop->maxfd-1; j >= 0; j--)
if (eventLoop->events[j].mask != AE_NONE) break;
eventLoop->maxfd = j;
}
}
void *aeGetFileClientData(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd) {
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) return NULL;
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];
if (fe->mask == AE_NONE) return NULL;
return fe->clientData;
}
int aeGetFileEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd) {
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) return 0;
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];
return fe->mask;
}
long long aeCreateTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long milliseconds,
aeTimeProc *proc, void *clientData,
aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc)
{
long long id = eventLoop->timeEventNextId++;
aeTimeEvent *te;
te = zmalloc(sizeof(*te));
if (te == NULL) return AE_ERR;
te->id = id;
te->when = getMonotonicUs() + milliseconds * 1000;
te->timeProc = proc;
te->finalizerProc = finalizerProc;
te->clientData = clientData;
te->prev = NULL;
te->next = eventLoop->timeEventHead;
te->refcount = 0;
if (te->next)
te->next->prev = te;
eventLoop->timeEventHead = te;
return id;
}
int aeDeleteTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id)
{
aeTimeEvent *te = eventLoop->timeEventHead;
while(te) {
if (te->id == id) {
te->id = AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID;
return AE_OK;
}
te = te->next;
}
return AE_ERR; /* NO event with the specified ID found */
}
/* How many microseconds until the first timer should fire.
* If there are no timers, -1 is returned.
*
* Note that's O(N) since time events are unsorted.
* Possible optimizations (not needed by Redis so far, but...):
* 1) Insert the event in order, so that the nearest is just the head.
* Much better but still insertion or deletion of timers is O(N).
* 2) Use a skiplist to have this operation as O(1) and insertion as O(log(N)).
*/
static int64_t usUntilEarliestTimer(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
aeTimeEvent *te = eventLoop->timeEventHead;
if (te == NULL) return -1;
aeTimeEvent *earliest = NULL;
while (te) {
if ((!earliest || te->when < earliest->when) && te->id != AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID)
earliest = te;
te = te->next;
}
monotime now = getMonotonicUs();
return (now >= earliest->when) ? 0 : earliest->when - now;
}
/* Process time events */
static int processTimeEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
int processed = 0;
aeTimeEvent *te;
long long maxId;
te = eventLoop->timeEventHead;
maxId = eventLoop->timeEventNextId-1;
monotime now = getMonotonicUs();
while(te) {
long long id;
/* Remove events scheduled for deletion. */
if (te->id == AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID) {
aeTimeEvent *next = te->next;
/* If a reference exists for this timer event,
* don't free it. This is currently incremented
* for recursive timerProc calls */
if (te->refcount) {
te = next;
continue;
}
if (te->prev)
te->prev->next = te->next;
else
eventLoop->timeEventHead = te->next;
if (te->next)
te->next->prev = te->prev;
if (te->finalizerProc) {
te->finalizerProc(eventLoop, te->clientData);
now = getMonotonicUs();
}
zfree(te);
te = next;
continue;
}
/* Make sure we don't process time events created by time events in
* this iteration. Note that this check is currently useless: we always
* add new timers on the head, however if we change the implementation
* detail, this check may be useful again: we keep it here for future
* defense. */
if (te->id > maxId) {
te = te->next;
continue;
}
if (te->when <= now) {
int retval;
id = te->id;
te->refcount++;
retval = te->timeProc(eventLoop, id, te->clientData);
te->refcount--;
processed++;
now = getMonotonicUs();
if (retval != AE_NOMORE) {
te->when = now + (monotime)retval * 1000;
} else {
te->id = AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID;
}
}
te = te->next;
}
return processed;
}
/* Process every pending file event, then every pending time event
* (that may be registered by file event callbacks just processed).
* Without special flags the function sleeps until some file event
* fires, or when the next time event occurs (if any).
*
* If flags is 0, the function does nothing and returns.
* if flags has AE_ALL_EVENTS set, all the kind of events are processed.
* if flags has AE_FILE_EVENTS set, file events are processed.
* if flags has AE_TIME_EVENTS set, time events are processed.
* if flags has AE_DONT_WAIT set, the function returns ASAP once all
* the events that can be handled without a wait are processed.
* if flags has AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP set, the aftersleep callback is called.
* if flags has AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP set, the beforesleep callback is called.
*
* The function returns the number of events processed. */
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
int processed = 0, numevents;
/* Nothing to do? return ASAP */
if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0;
/* Note that we want to call aeApiPoll() even if there are no
* file events to process as long as we want to process time
* events, in order to sleep until the next time event is ready
* to fire. */
if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 ||
((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) {
int j;
struct timeval tv, *tvp = NULL; /* NULL means infinite wait. */
int64_t usUntilTimer;
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL && (flags & AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP))
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
/* The eventLoop->flags may be changed inside beforesleep.
* So we should check it after beforesleep be called. At the same time,
* the parameter flags always should have the highest priority.
* That is to say, once the parameter flag is set to AE_DONT_WAIT,
* no matter what value eventLoop->flags is set to, we should ignore it. */
if ((flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) || (eventLoop->flags & AE_DONT_WAIT)) {
tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0;
tvp = &tv;
} else if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) {
usUntilTimer = usUntilEarliestTimer(eventLoop);
if (usUntilTimer >= 0) {
tv.tv_sec = usUntilTimer / 1000000;
tv.tv_usec = usUntilTimer % 1000000;
tvp = &tv;
}
}
/* Call the multiplexing API, will return only on timeout or when
* some event fires. */
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
/* Don't process file events if not requested. */
if (!(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) {
numevents = 0;
}
/* After sleep callback. */
if (eventLoop->aftersleep != NULL && flags & AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP)
eventLoop->aftersleep(eventLoop);
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fired = 0; /* Number of events fired for current fd. */
/* Normally we execute the readable event first, and the writable
* event later. This is useful as sometimes we may be able
* to serve the reply of a query immediately after processing the
* query.
*
* However if AE_BARRIER is set in the mask, our application is
* asking us to do the reverse: never fire the writable event
* after the readable. In such a case, we invert the calls.
* This is useful when, for instance, we want to do things
* in the beforeSleep() hook, like fsyncing a file to disk,
* before replying to a client. */
int invert = fe->mask & AE_BARRIER;
/* Note the "fe->mask & mask & ..." code: maybe an already
* processed event removed an element that fired and we still
* didn't processed, so we check if the event is still valid.
*
* Fire the readable event if the call sequence is not
* inverted. */
if (!invert && fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
fired++;
fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; /* Refresh in case of resize. */
}
/* Fire the writable event. */
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc) {
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
fired++;
}
}
/* If we have to invert the call, fire the readable event now
* after the writable one. */
if (invert) {
fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; /* Refresh in case of resize. */
if ((fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) &&
(!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc))
{
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
fired++;
}
}
processed++;
}
}
/* Check time events */
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS)
processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop);
return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */
}
/* Wait for milliseconds until the given file descriptor becomes
* writable/readable/exception */
int aeWait(int fd, int mask, long long milliseconds) {
struct pollfd pfd;
int retmask = 0, retval;
memset(&pfd, 0, sizeof(pfd));
pfd.fd = fd;
if (mask & AE_READABLE) pfd.events |= POLLIN;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) pfd.events |= POLLOUT;
if ((retval = poll(&pfd, 1, milliseconds))== 1) {
if (pfd.revents & POLLIN) retmask |= AE_READABLE;
if (pfd.revents & POLLOUT) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE;
if (pfd.revents & POLLERR) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE;
if (pfd.revents & POLLHUP) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE;
return retmask;
} else {
return retval;
}
}
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|
AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP|
AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);
}
}
char *aeGetApiName(void) {
return aeApiName();
}
void aeSetBeforeSleepProc(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep) {
eventLoop->beforesleep = beforesleep;
}
void aeSetAfterSleepProc(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, aeBeforeSleepProc *aftersleep) {
eventLoop->aftersleep = aftersleep;
}소스를 보면 System Call관련 내용과 Event Loop 내용들이 있습니다.
ae_epoll.c는 api 이벤트 관련 즉 클라이언트에서 들어오는 이벤트를 감지하는 역할인거 같고
ae.c는 Event Loop관련 내용인거 같습니다.
결론 : epoll 같은 시스템 콜은 이벤트를 감시!
Event Loop를 돌면서 준비된 애들만 빠르게 처리!
ex) epoll이 감시하는 대상은 소켓 FD(File Descriptor)이고 클라이언트가 데이터를 보내면 OS 커널이 소켓 버퍼에 데이터를 쌓아두고
읽을 준비가 됨(EPOLLIN)이라는 신호를 만들어줍니다.
ae_epoll.c 소스에 아래와 같은 내용 참고!!
- 읽기 가능 / EPOLLIN / 소켓 버퍼에 클라이언트 데이터가 들어옴(read 가능)
- 쓰기 가능 / EPOLLOUT / 소켓이 쓰기 가능한 상태(write 가능)
- 예외 발생 / EPOLLERR, EPOLLHUP / 연결 끊김, 에러
ee.events = 0;
mask |= eventLoop->events[fd].mask; /* Merge old events */
if (mask & AE_READABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLIN;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLOUT;
ee.data.fd = fd;
...
numevents = retval;
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
int mask = 0;
struct epoll_event *e = state->events+j;
if (e->events & EPOLLIN) mask |= AE_READABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLOUT) mask |= AE_WRITABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLERR) mask |= AE_WRITABLE|AE_READABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLHUP) mask |= AE_WRITABLE|AE_READABLE;
eventLoop->fired[j].fd = e->data.fd;
eventLoop->fired[j].mask = mask;
}Task Queue는 fired[]이고 data.fd와 mask(AE_READABLE 등)가 들어간다.
그래서 이벤트 감시라는건 OS 커널에서 주는 신호를 감지하고 그 데이터들을 이벤트루프에서 처리한다!!
또한 싱글쓰레드라서 context switching, 쓰레드 전환이 없고 들어오는 데이터들에 대해서 동시게 감시를 하는데
이 감시는 지금 처리해야하는 것만 커널이 골라서 알려준다!(준비 된 것만 처리!)
그래서 개빠름!!
제대로 알아보려면 디버깅하면서 보면 좋은데 여기까지 하겠습니다 ㅋㅋㅋ
더 관심 있으신분들은 파고~파고~

Event Loop
마지막으로 Event Loop에 대해서 알아보겠습니다.
Event Loop는 이벤트가 발생할 때까지 기다리다가 이벤트가 생기면 그에 맞는 처리 함수를 호출하고
다시 기다리는 반복(Loop) 구조 입니다.

Non-Blocking I/O + OS커널(epoll) + Event Loop 삼대장을 조금 디테일하게 그려보면 아래와 같습니다.
'OpenSource > Redis' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DelayQueue란? (feat. Java표준, Redis) (0) | 2025.11.24 |
|---|---|
| Redis에서 TTL이 expired(만료)되면 메모리에 데이터는 아직 있다? 없다? (0) | 2025.11.06 |
| Redis Cache 연동(Spring Boot) (0) | 2024.08.23 |
| local에 Docker 기반 Redis 셋팅(feat. mac) (0) | 2022.04.12 |
| redis 메모리 사용량? (0) | 2016.01.27 |



